

The scaphoid is found in the wrist and foot - though many use the word The greater multangular), some appear twice (e.g., the navicular, also known as

Obscure (medial cuneiform), some have two names (the trapezium is also known as NOTE: The precursor of all nomenclature is the name of theīone - it is imperative to learn them all. Greenstick/buckle: partial fractures in children,.Pathological: underlying bone is not normal (e.g., tumor),.Obtaining follow-up radiographs has been proved useful for diagnosing fractures of the ribs and long bones, where the signs of fracture healing that allow the diagnosis may require time to develop. Long bone fractures in the limbs can be characterized in. Periarticular: near and likely involving a joint, Fractures of the spine, pelvis, and hands are exceedingly rare 6, 7. LONGBONE FRACTURES: Putting Humpty Dumpty back together again. Traumatic injury and fracture is one of the world's leading causes of death and disability (Haagsma 2016).Acute orthopaedic injuries, including soft tissue, muscle and bone injuries, are the most common injuries sustained in accidents and the most likely form of traumatic injury to require hospitalisation (Clay 2010 Lang 20).(The older term for this is a "compound fracture".) Lacerated or abraded the fracture is exposed to the outside environment. Open: skin/soft tissue over and near the fracture is.Closed: skin/soft tissue over and near fracture is intact,.
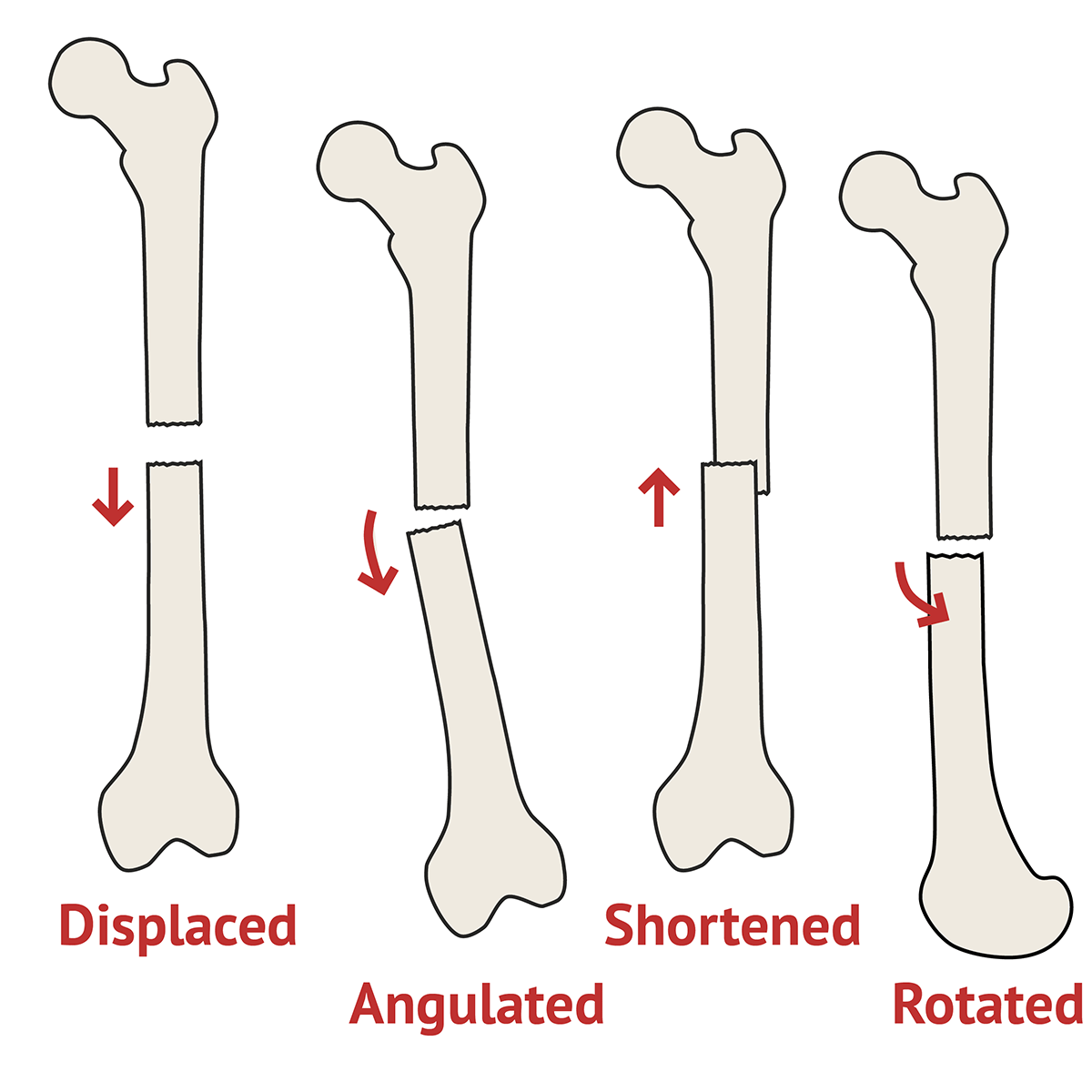
A fracture occurring in this area would be described as a "diaphyseal fracture".įigure 11: Spiral meta-diaphyseal (extending into both metaphyseal and diaphyseal segments) distal tibia fracture, displaced into varus (distal fragment is medial). This is furtherĬategorized as proximal, middle, or distal diaphysis, Shown in yellow. Diaphyseal: The shaft of the long bone.A fracture occurring in this area would be described as a "metaphyseal fracture". Metaphysis: the “flared” portion of the bone between theĮpiphysis and the shaft, Shown in purple.A fracture occurring in this area would be described as an "epiphyseal fracture". Epiphysis: the ends of the bone forming part of the jointĪrticulation, Shown in green.A hip fracture is a break in the upper quarter of the femur (thigh) bone. A fracture occurring in this area would be described as a "physeal fracture". Common types of bone fractures and possible symptoms. (once growth plate fuses in adult), Shown in red. Physis (growth plate in growing child) or “Physeal scar”.(4) soft tissue envelope, each of which are expanded upon below. The tibia and fibula are the two smaller bones located in the lower leg. Location (region) within the bone, (2) fracture pattern, (3) displacement and The femur bone, or thigh bone, is the long bone that runs from the hip to the knee. There are four main components to fracture description: (1) Medical communication as well as clinical decision-making regarding management Accurate clinical description of a fracture is vital for


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
